
By Kate Abnett and Simon Jessop
SHARM EL-SHEIKH, Egypt (Reuters) – A G7-led plan dubbed “Global Shield” to provide funding to countries suffering climate disasters was launched at the U.N. COP27 summit on Monday, although some questioned the effectiveness of the planned scheme.
Coordinated by Group of 7 president Germany and the V20 group of climate-vulnerable countries, it aims to rapidly provide pre-arranged insurance and disaster protection funding after events such as floods, droughts and hurricanes hit.
Backed by 170 million euros ($175.17 million) in funding from Germany and 40 million euros from other donors including Denmark and Ireland, the Global Shield will in the next few months develop support to be deployed in countries including Pakistan, Ghana, Fiji and Senegal when events occur.
Some countries and campaigners were cautious, however, concerned it risked damaging efforts to secure a substantive deal on financial help for so-called “loss and damage” – the U.N. jargon for irreparable damage wrought by global warming.
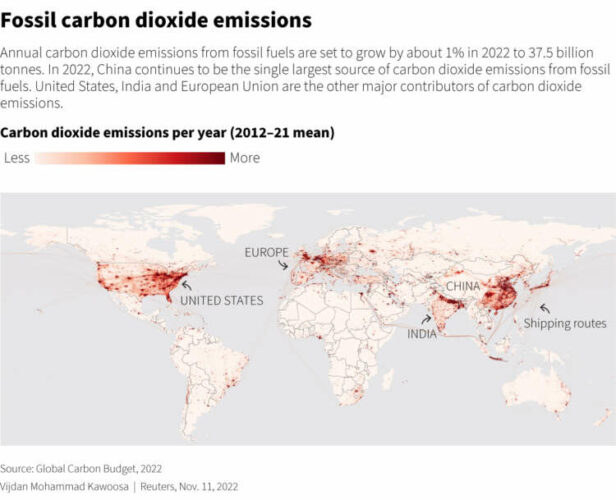
(Graphic: Fossil carbon dioxide emissions – https://graphics.reuters.com/CLIMATE-UN/CARBON-BUDGET/klvygexwbvg/graphic.jpg)
German development minister Svenja Schulze said the Global Shield aimed to complement, not replace, progress on loss and damage.
“It is not a kind of tactic to avoid formal negotiation on loss and damage funding arrangements here,” Schulze said. “Global Shield isn’t the one and only solution for loss and damage. Certainly not. We need a broad range of solutions.”
Some research suggests that by 2030, vulnerable countries could face $580 billion per year in climate-linked “loss and damage”.
Ghana’s finance minister Ken Ofori-Atta, who chairs the V20 group of vulnerable countries, called the creation of the Global Shield “long overdue”.
Yet some vulnerable countries questioned the scheme’s focus on insurance, with insurance premiums adding another cost to cash-strapped countries that have low carbon emissions and contributed least to the causes of climate change.
“We are not yet persuaded, especially of the insurance elements,” Avinash Persaud, Special Envoy on Climate Finance to Barbados Prime Minister Mia Mottley, told Reuters.
“Using insurance is a method in which the victim pays, just in instalments in the beginning,” he said, adding that loss and damage finance should be grant-based.
It was not immediately clear how much of the Global Shield funding announced so far was in grant form.
Michai Robertson, a negotiator for the Alliance of Small Island States – which is championing calls for a new U.N. loss and damage fund in the talks this week – said even subsidised insurance premiums could enable insurance companies in wealthy countries to profit off poor and vulnerable nations’ suffering.
“There’s an inherent injustice about them profiting off of our loss and damage,” he said.
($1 = 0.9705 euros)
For daily comprehensive coverage on COP27 in your inbox,
sign up for the Reuters Sustainable Switch newsletter here
(Additional reporting by Valerie Volcovici; Editing by Frank Jack Daniel)


